Learn how a self-service knowledge base improves customer satisfaction, cuts support costs, and streamlines operations. Build smarter support with expert strategies and tools.
Every day, your customers are making silent decisions.
They’re choosing between waiting in support queues or finding their own answers. The ones who succeed on their own feel empowered—and more loyal.
The ones who don’t? They churn quietly, never telling you why.
A self-service knowledge base isn’t just a helpful resource; it’s your frontline in this silent battle—cutting costs, boosting satisfaction, and proving you understand what modern customers actually want: control, speed, and clarity.
In this detailed blog post, we will explore what a self-service knowledge base is, its importance, key components, and practical steps required to build and optimize one. We will also delve into advanced strategies involving AI and automation, analyze common challenges, and look at the future of knowledge management and why it can be the saving grace of a company in testing times.
What Is a Self-Service Knowledge Base?
A self-service knowledge base (KB) is a centralized digital repository of information designed to enable customers and employees to find answers to their questions independently.
Unlike traditional knowledge bases, which may serve only internal users or lack user-friendly interfaces, self-service knowledge bases emphasize accessibility, ease of search with intuitive navigation, and comprehensive coverage of product, service, and process information.
Its whole purpose is to present the simplest of replies to even the most complex of queries.
Such a knowledge base improves customer experience by reducing the need for direct support interaction and allowing faster problem resolution.
It also saves a lot of human effort and time that comes with some queries. It typically includes content such as FAQs, how-to articles, troubleshooting guides, video tutorials, user manuals, runbooks, glossaries, and data sheets.
Differentiating concepts:
- General knowledge bases: Often internal and less focused on user experience, in most cases, it is best suited to employees or experts.
- Self-service: As the name suggests, such platforms or channels let users help themselves with simple navigation.
- Self-Service Knowledge Base: A structured, searchable engine that supports self-service queries by delivering timely, relevant knowledge content.
At its most truest, a self-service knowledge base serves as an immediate information hub that customers can visit before contacting support. This not only saves time, especially for common queries, but ensures a brand exercise that showcases a company as customer-centric.
Why Is a Self-Service Knowledge Base Important?
The importance of a self-service knowledge base spans multiple dimensions that benefit businesses, customers, and the overall customer service ecosystem.
Benefits for Businesses and Customers

- 24/7 Accessibility: Customers can resolve issues anytime, thus increasing convenience and satisfaction metrics.
- Cost Reduction: By deflecting standard queries, support teams focus on complex tasks and workflow improvements that reduce operational expenses.
- Speed and Efficiency: Rapid access to relevant information minimizes wait times and increases first-contact resolution.
- Consistent Information Delivery: Prevents misinformation by providing authoritative, up-to-date content.
- Customer Empowerment: Give users the choice to control their support experience by self-navigating resources and relevant subsequent channels, if necessary.
Role in Customer Service and Contact Centers
Much of the influx in support channels is generally routine inquiries, which make up to 40% of the workload.
With a self-service knowledge base, these routine inquiries are handled efficiently, thereby decreasing agent workload and improving KPIs like reduced average handle time and improved overall service levels. Also, the time saved on routine inquiries allows human agents to fine-tune their learning with extensive investment in R&D for complex scenarios.
Impact on Customer Experience and Satisfaction
A recent study highlighted that 69% of consumers attempt to resolve issues on their own before seeking live help. A well-researched and thorough knowledge base can aid this quest of consumers and can create a foundation that leads to better ratings, increased loyalty, and a stronger brand reputation as customers get what they want, i.e., a fast and simple-to-understand issue resolution mechanism.
Key Components of an Effective Self-Service Knowledge Base
A bona fide self-service knowledge base combines content relevance, accessibility, and seamless integration with complementary tools that make subsequent users’ actions easier.
Essential Knowledge Elements and Content Types
The knowledge base should include:
- FAQs: Address common, straightforward questions.
- Troubleshooting Guides: Step-by-step documentation for problem resolution.
- User Manuals & How-To Articles: Comprehensive instructions for product/service use case.
- Video Demonstrations: Short (approx. 2 minutes) visual guides that enhance understanding of products and their capabilities.
- Glossaries: Clarify technical or industry-specific terminology.
- Runbooks: For IT or administrative process standardization.
- Specification Sheets: Detailed technical details of product and service configurations.
The prior research for creating a well-equipped knowledge base can be done by analyzing support tickets, chatbot interactions, and search queries put in by the users. This creates a self-help guide that is rooted in actual user experience and comprises questions that more or less meet the general expectation of user needs, minimizing guesswork.
Structure and Navigation Best Practices
- Categorization: Organize information into categories and subcategories.
- Search Functionality: Create search bars with natural language processing (NLP) to improve content discoverability with exact and related search terms.
- Simplicity: Use clear, concise language and visuals to enhance concept understanding.
- Accessibility: Ensure easy access via website widgets, mobile apps, and portals.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Enable users to rate articles and submit comments for continuous improvement. Allow users to build a community where they can contribute to fellow customers’ queries, citing their self-help experience.
Integration with Other Self-Service Tools
Seamless navigation to solutions is an important trait for a self-service knowledge base. And this gets achieved with how knowledge bases integrate with:
- AI Chatbots: To deliver contextual answers and guide users to relevant articles and sections.
- Customer Portals: Provide personalized access to user-specific data and knowledge.
- Community Forums: Foster peer-to-peer support to enhance engagement.
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR) Systems: Link callers to appropriate self-help content.
The fusion of tech with a knowledge base improves the efficacy of query resolution. The availability of multi-channel consistency ensures that users receive coherent and efficient support no matter which platform they engage with.
See AI-Powered Replies in Action
How a Self-Service Knowledge Base Supports Customer Self-Service Channels
A robust self-service knowledge base forms a crucial pillar of the customer support ecosystem. With a plethora of users always in line to get their tickets addressed, a self-help service channel can take a good burden off the overwhelmed human agents, especially during peak season. Here are the various ways a knowledge base supports ongoing customer service efforts.
Relationship with FAQs, Community Forums, IVRs, and Mobile Apps
While FAQs provide quick and short answers to the pain points, they often lack depth and interactivity from a technical point of view.
Knowledge bases expand on FAQs with detailed content and multimedia support, allowing users to research with a slightly in-depth practical understanding of their searched topic.
Community forums enable dynamic peer interactions, with knowledge bases serving as an official reference to prevent misinformation. It also acts as a public portal where fellow users can verify the legitimacy of support information present on the knowledge base portal. I
VR systems can direct users to relevant articles, reducing the pipeline pressure on live agent calls. And, mobile apps with their remote support and personalized push notifications give users redirection to the relevant articles in context to their support queries.
Enhancing Multi-Channel Consistency and Accessibility
With much of the traffic now online, the support infrastructure has also shifted big-time to the servers. Customers with their presence across multiple channels demand seamless service across devices and platforms. It’s in scenarios like this that a unified knowledge base linked with all channel touchpoints becomes the most proficient tool for a customer support structure. It allows:
- Consistent answers regardless of channel
- Reduced frustration from conflicting information
- Improved customer engagement by meeting users “where they are”
Not to mention, in today’s omnichannel market, having self-service access across portals and platforms is a defining characteristic of modern customer service.
Now, let’s move on to some common challenges in self service knowledge base implementation.
Challenges and Common Mistakes in Self-Service Knowledge Base Implementation
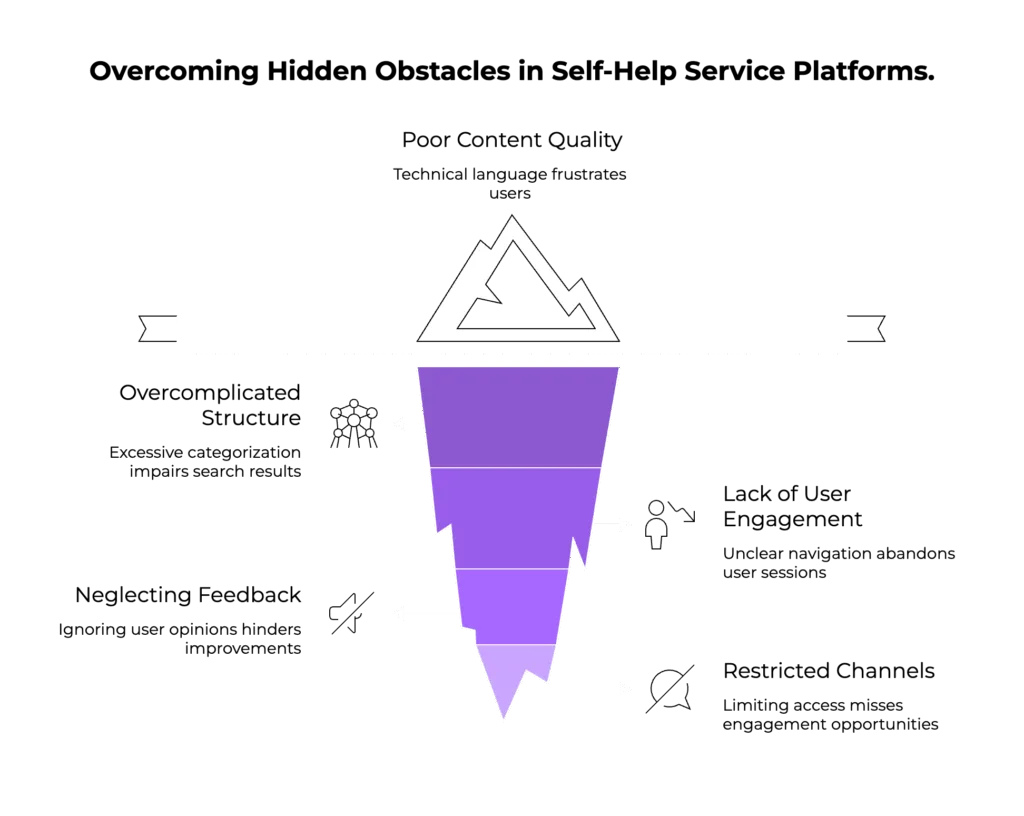
It may be simple to execute, but from a data logistics perspective, creating and maintaining a knowledge database comes with its own set of challenges.
Typical Obstacles and How to Avoid Them
- Poor Content Quality: One should refrain from using overly technical language or outdated information that may frustrate users. Stakeholders should regularly pursue audits and customer feedback to address this issue.
- Overcomplicating Structure: Excessive categorization or indexed content impairs search results. Ensure the results are easy to find by implementing KISS (Keep It Simple Stupid) principles.
- Lack of User Engagement: Design the layout of the search engine with clear navigation. This keeps the users interested and avoids regularly abandoned sessions.
- Neglecting Feedback: Always lend an ear to what users think about your self-help service platform. Take the insights for continuous improvements to improve data accessibility.
- Restricted Mobile and Social Channels: Keep the knowledge bases open through multiple channels, such as social media and mobile app support. This caters to channel-specific audiences and cashes in on vital engagement opportunities.
Now, let’s move on to some best practices of creating an effective knowledgebase.
Best Practices for Creating an Effective Self-Service Knowledge Base
Implementing an all-season self-service knowledge base demands a fine-tuned content strategy, user-centric design, and an ongoing improvement cycle.
Content Creation Tips to Ensure Clarity and Usefulness
- Start collating content based on FAQs, support tickets, and chatbot data.
- Use plain language and avoid jargon to maximize content accessibility.
- Incorporate visual aids such as screenshots and videos.
- Prioritize short sentences as they improve readability.
Making Content Easy to Find and Understand
- Use search widgets that can detect misspellings and accurately match intended search queries.
- Organize content with proper logical hierarchies and tagging.
- Enable article ratings and customer feedback with comments to identify gaps in content.
Regularly Updating and Maintaining Content Quality
- Schedule periodic reviews linked to product updates or customer feedback.
- Empower cross-team collaboration between support, marketing, and product departments.
- Automate notifications for less-visited pages to trigger revisions.
How to Create a Self-Service Knowledge Base: Step-by-Step Guide

Launching an effective knowledge base follows these steps:
1. Define Purpose and Scope
Know the audience first. Determine who the knowledge base primarily serves. Is it external customers, internal employees, or both? Clarify these goals, as they set the foundation for other processes to follow, including content creation and collation, search index development, technical details, and more.
2. Identify Key Content Areas
Be mindful of key content areas that require input from other customer support setups. This improves accessibility to relevant data and aligns topics with user needs.
3. Plan Structure
Design a simple search algorithm with the development team, keeping in mind:
- Search bar with Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Content management and version control
- Analytics and feedback collection
- Integration capabilities (e.g., chatbots, portals)
4. Build a Knowledge Management Team
Include cross-functional members with customer support expertise. These profiles comprise support agents, subject matter experts, content writers, technical writers, and IT specialists. All this collaboration fosters a high-quality knowledge base.
5. Integrate With Communities and Other Platforms
Once the knowledge platform content is live, the next goal should be to maximize its reach with forums, mobile apps, social channels, and IVRs. This approach maximizes impressions among the intended target group, which is present across all channels.
Measuring and Improving the Effectiveness of Your Knowledge Base
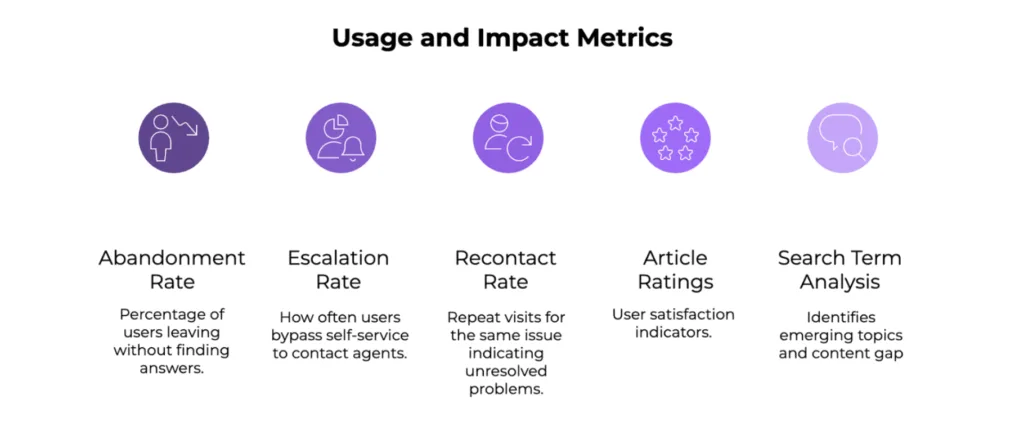
Analytics is a key aspect in determining whether all your effort has yielded the intended results or not. To uncover gaps in the quality of content, regular review benefits big time.
Metrics to Track and Analyze Usage and Impact
- Abandonment Rate: Percentage of users ending the session without finding answers.
- Escalation Rate: How often users bypass the self-service portal to contact agents directly.
- Recontact Rate: Count of repeat visits for the same issue, highlighting unresolved problems, and perhaps, navigation issues.
- Article Ratings and Feedback: User satisfaction indicators.
- Search Term Analysis: Identifies emerging topics and content gaps.
Using Feedback and AI-Powered Tools to Keep Knowledge Fresh
Artificial Intelligence can be a helping hand in sorting out some improvement metrics:
- Analyze customer comments for sentiment and trends.
- Automate content update reminders.
- Offer proactive suggestions and personalized article recommendations.
Continuous Improvement Strategies
- Regularly review analytics and user feedback.
- Test content formats with A/B testing.
- Train staff to contribute fresh insights based on their interactions with users.
- Prioritize updating high-traffic/low-rated articles.
Emerging Trends and Technologies
- Contextual Knowledge: Delivering relevant content based on real-time user actions.
- Mobile-First Design: Ensuring flawless access on smartphones and tablets with an intuitive UI.
- Social and Collaborative Features: Allow community interaction within knowledge platforms.
- Voice Search and Virtual Assistants: Integrating voice-based search in knowledge bases.
- Proactive Engagement: Automated prompts and chat pop-ups that act proactively according to user needs.
Harnessing Customer Feedback to Refine Your Knowledge Base
As an ongoing process for constructive improvements in knowledge base content, allowing customer feedback is the biggest tick. Companies that keep the forum open to comments from their users can:
- Identify pain points customers face in navigation and content comprehension.
- Prioritize high-impact content improvements.
- Detect new issues emerging from product updates or market changes.
- Measure self-service effectiveness and inform support staff.
A conglomerate that regularly seeks improvement from its user base with surveys, article ratings, and behavior analytics has more chances of success in meeting customer expectations.
Creating a self-service knowledge base acts as more than just a repository. It is a smart step in keeping up with the ever-evolving customer satisfaction metrics by providing them with what they need in a timely manner.
It also fuels the strategic aspect of a company’s future policies that continue to push boundaries of superior customer experience, operational efficiency, and scalable support. Companies that continue to prioritize relevant content with integration of artificial intelligence capabilities and upskilling of their workforce can achieve:
- Reduced support costs and agent workload
- Enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty
- Accelerated onboarding and employee productivity
- Unified, accessible information across all customer touchpoints
The main things to remember are that creating a knowledge base is one aspect, while keeping it regularly updated is another. Organizations that ensure attention towards users’ needs can find themselves evolving organically with revised metrics of customer satisfaction in today’s online ecosystem. Giving you an edge over your competition, a knowledge base future-proofs your standing as a self-reliant, digital-first brand.